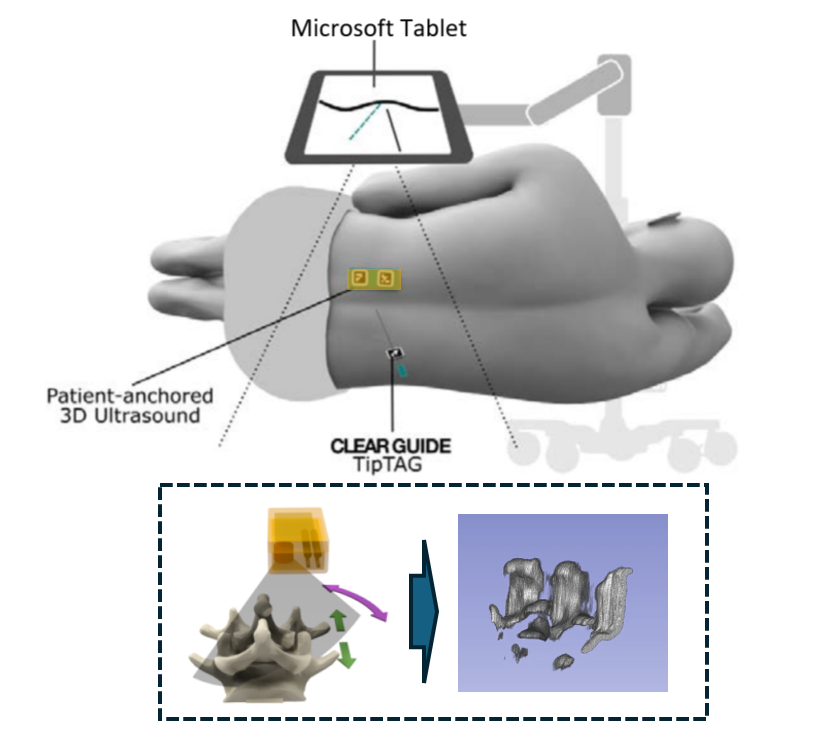
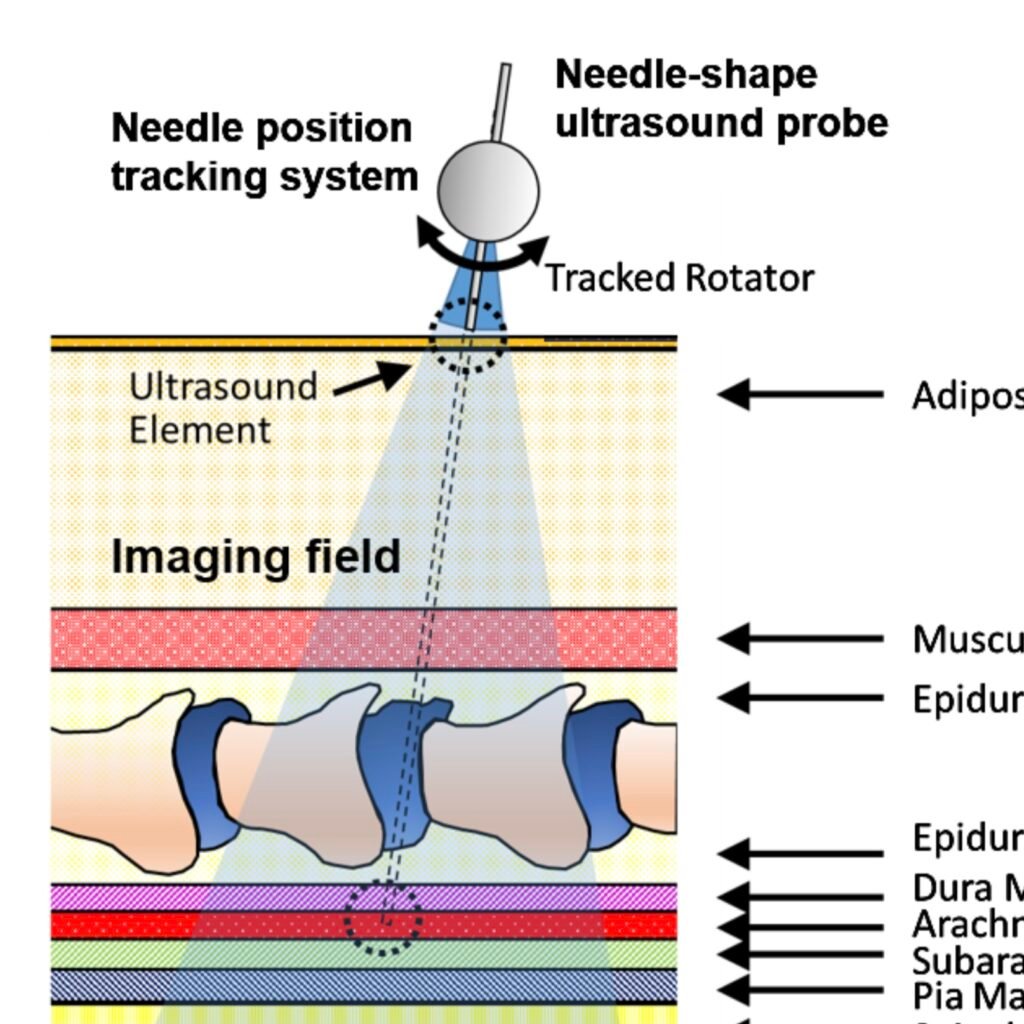
As one of the most commonly performed spinal interventions in routine clinical practice, lumbar punctures are usually done with only hand palpation and trial-and-error. Failures can prolong procedure time and introduce complications such as cerebrospinal fluid leaks and headaches. Therefore, in this work, we present a complete lumbar puncture guidance system with the integration of…
Tag: ultrasonically smart tools
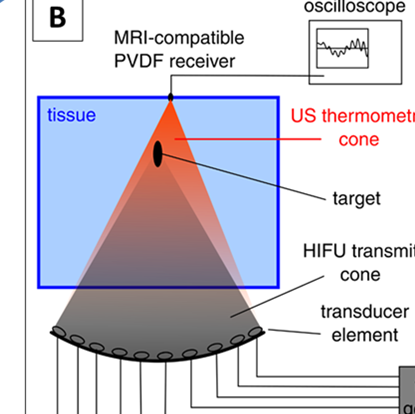
Our innovative research is focused on determining if US tomography-based thermometry in combination with thermal and acoustic modelling can be sufficient to replace MR thermometry and hence devising a system that can perform the same safe and effective uterine fibroid ablations without the need for costly MRI. Our developed system leverages existing HIFU systems by…
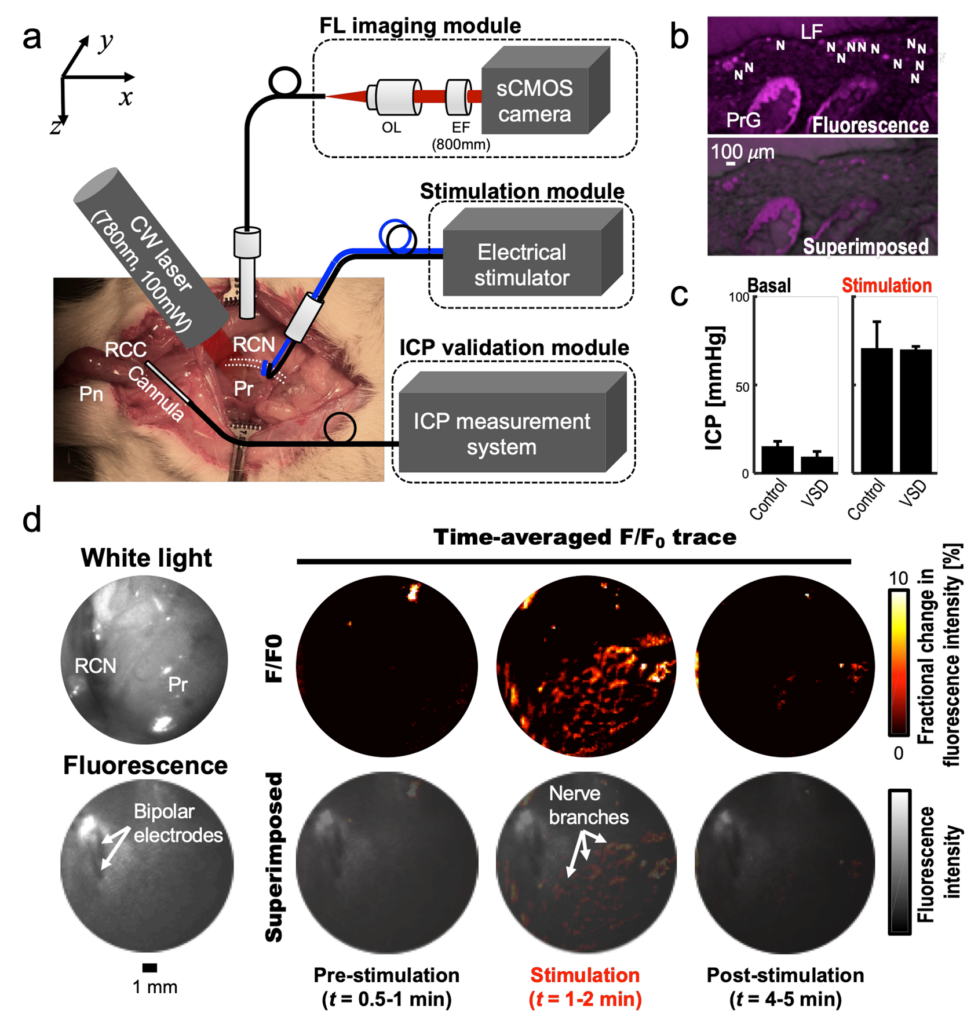
Sparing nerve during surgical procedure such as radical prostatectomy is crucial in minimizing post-operative complication. In this project, we aim to provide intra-operative functional nerve localization. Voltage-sensitive-dye imaging was developed by using fluorescence (FL) and photoacoustic (PA) imaging, where the optical contrast upon membrane potential variation was identified. In particular, PA imaging showed depth-profiling of…
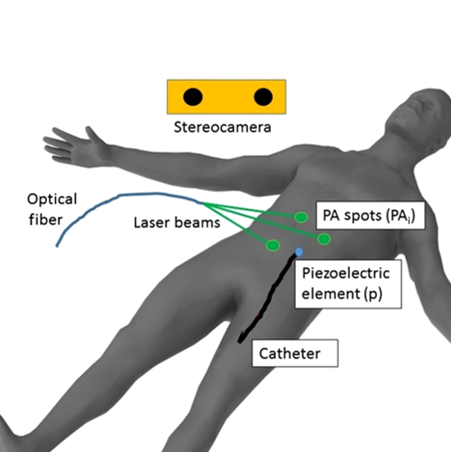
Needles, guidewires, and catheters represent some of the most used daily instruments by interventional radiologists. Catheters are commonly tracked with either an imaging modality such as X-ray fluoroscopy or a tracking system such as electromagnetic (EM) trackers. X-ray delivers a radiation dosage to the patient for a non-therapeutic purpose; and an EM tracker places certain…
For clinical diagnosis and surgical monitoring and guidance, many imaging modalities are able to non-invasively show regional anatomy and position details, but few of them are able to provide functional information. Monitoring the concentration of metabolism-related species or bio-markers could also be helpful during surgery and in interventional imaging. For example, to determine whether the…
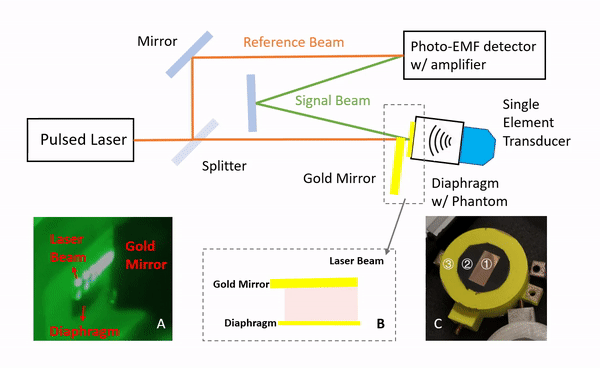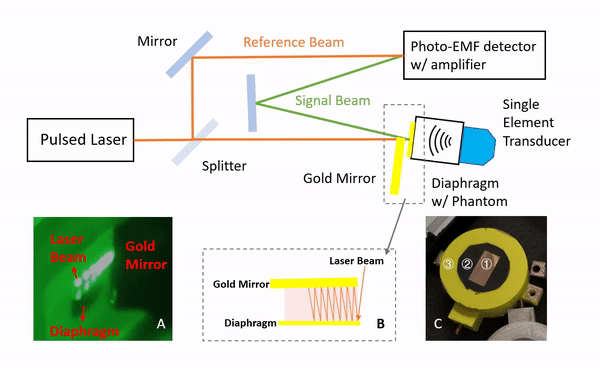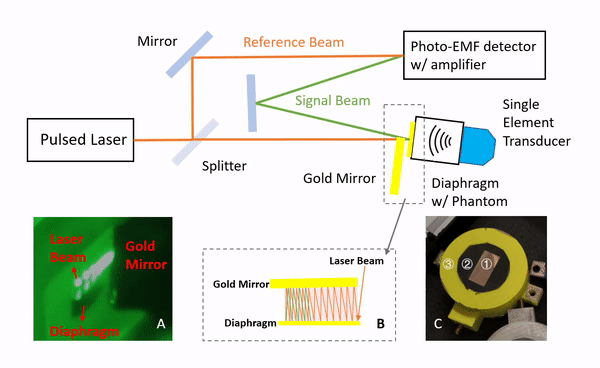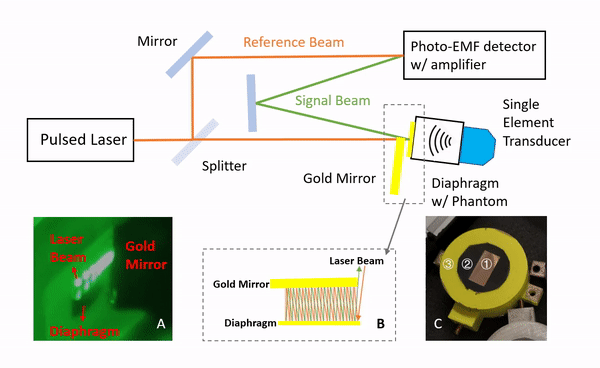
Lumbar punctures (LPs) are interventional procedures that are used to collect cerebrospinal fluid. Since the target window is small, physicians have limited success conducting the procedure. The procedure is especially difficult for obese patients due to the increased distance between bone and skin surface. We propose a simple and direct needle insertion platform, enabling image formation by sweeping a needle with a single ultrasound element at the tip. The needle-shaped ultrasound transducer can not only sense the distance between the tip and a potential obstacle, such as bone, but also visually locate the structures by combining transducer location tracking and synthetic aperture focusing. The concept of the system was validated through a simulation that revealed robust image reconstruction under expected errors in tip localization. The initial prototype was built into a 14 G needle and was mounted on a holster equipped with a rotation shaft allowing one degree-of-freedom rotational sweeping and a rotation tracking encoder. We experimentally evaluated the system using a metal-wire phantom mimicking high reflection bone structures and human spinal bone phantom. Images of the phantoms were reconstructed, and the synthetic aperture reconstruction improved the image quality. These results demonstrate the potential of the system to be used as a real-time guidance tool for improving LPs.