Sparing nerve during surgical procedure such as radical prostatectomy is crucial in minimizing post-operative complication. In this project, we aim to provide intra-operative functional nerve localization. Voltage-sensitive-dye imaging was developed by using fluorescence (FL) and photoacoustic (PA) imaging, where the optical contrast upon membrane potential variation was identified. In particular, PA imaging showed depth-profiling of the deep nerve tissue. Real-time imaging was conducted with a clinical ultrasound system integrated with da Vinci SI surgical robot. We have leveraged the iPASS technology, where a single optical fiber generates multiple photoacoustic markers (PM) to register the da Vinci endoscope camera and the US/PA imaging. The PM technology not only enables the frame registration between the two imaging frames, but also provides the tracked imaging of the target tissue to enable continuous monitoring.
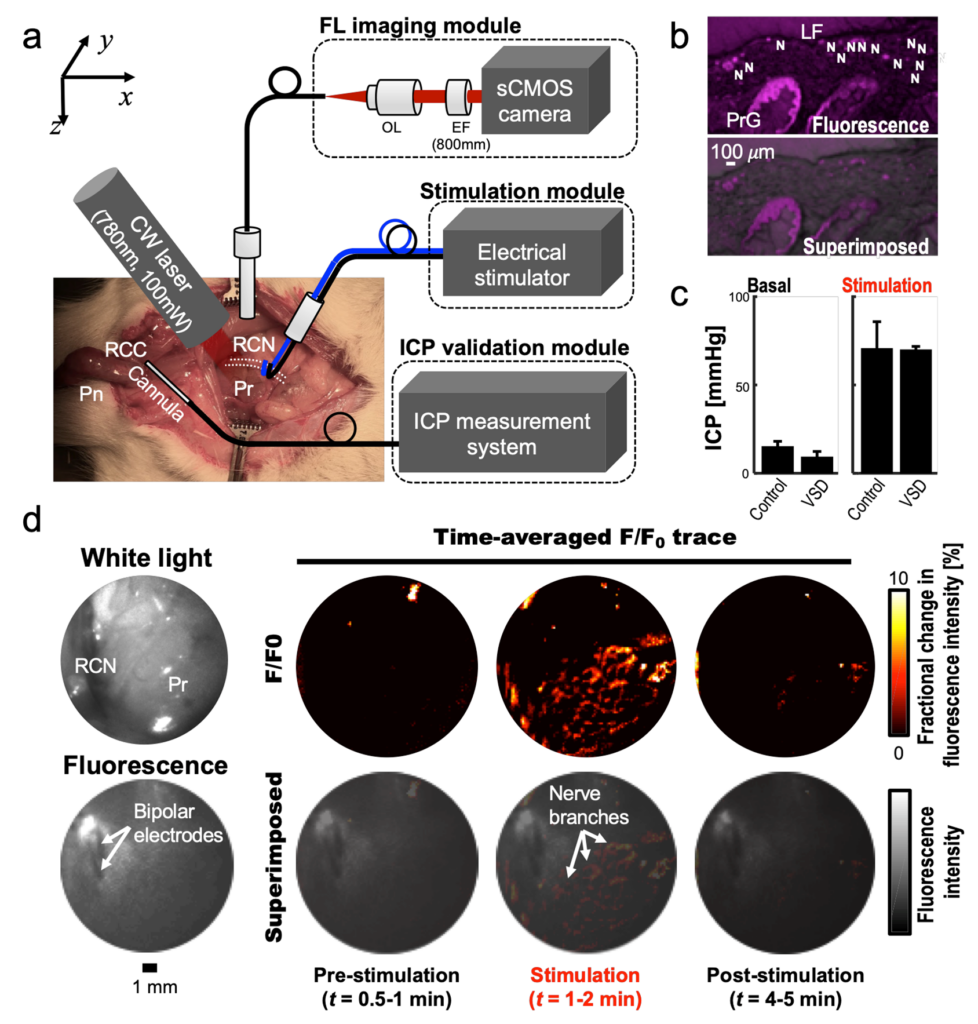
Intra-operative FL imaging of rat prostatic nerve network in vivo
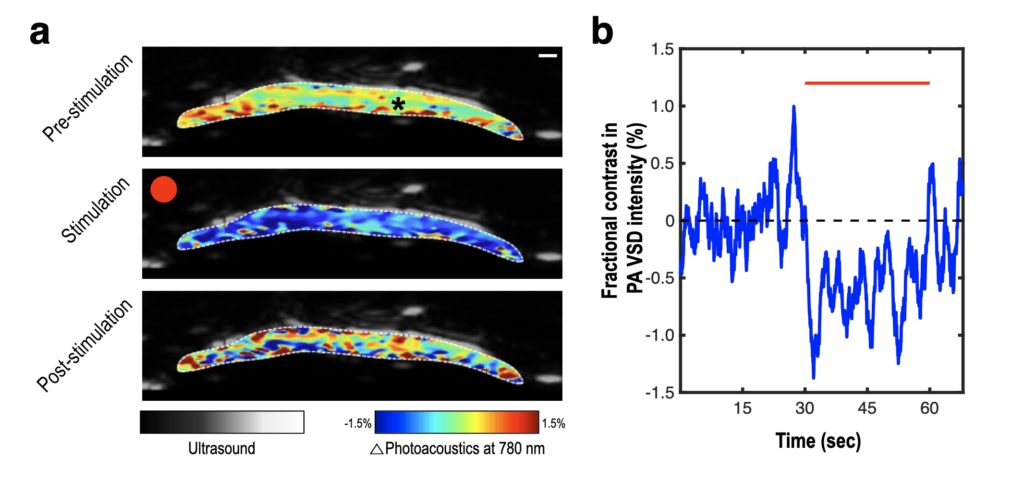
Photoacoustic voltage-sensitive dye imaging of piglet sciatic nerve
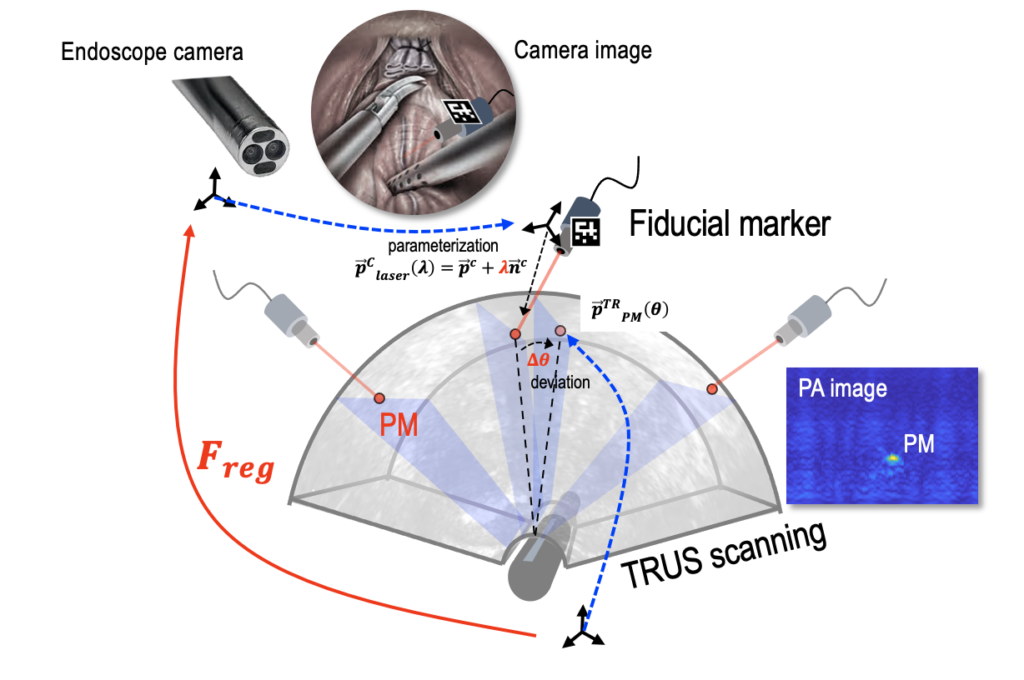
Integration of US system to da Vinci SI surgical robot
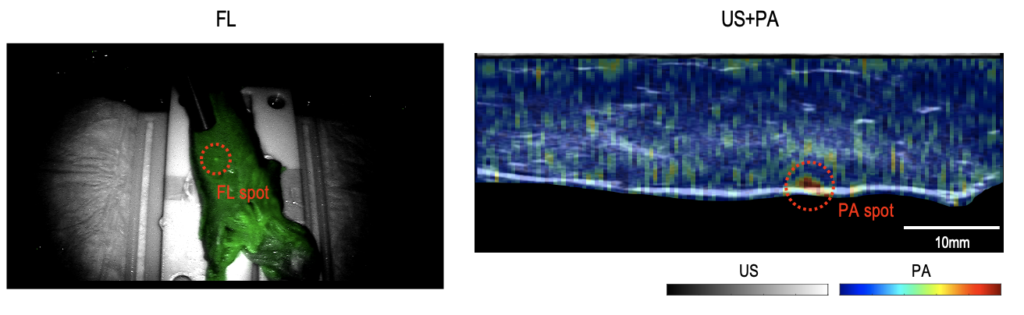
For more information, please contact hsong37@jhu.edu
Publications
- Song, H., Yang, S., Wu, Z., Moradi, H., Taylor, R. H., Kang, J. U., … & Boctor, E. M. (2024). Arc-to-line frame registration method for ultrasound and photoacoustic image-guided intraoperative robot-assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy. International Journal of Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery, 19(2), 199-208.
- Song, H., Moradi, H., Jiang, B., Xu, K., Wu, Y., Taylor, R. H., … & Boctor, E. M. (2022). Real-time intraoperative surgical guidance system in the da Vinci surgical robot based on transrectal ultrasound/photoacoustic imaging with photoacoustic markers: an ex vivo demonstration. IEEE robotics and automation letters, 8(3), 1287-1294.
- Song, H., Kang, J., & Boctor, E. M. (2022, March). Functional guidance of nerve graft surgery using dual-modal photoacoustic and fluorescence imaging of voltage-sensitive dye: ex vivo proof-of-concept study. In Multimodal Biomedical Imaging XVII (Vol. 11952, pp. 28-34). SPIE.
- Kang J, Le HND, Karakus S, Malla AP, Harraz MM, Kang JU, Burnett AL, Boctor EM. Real-time, functional intra-operative localization of rat cavernous nerve network using near-infrared cyanine voltage-sensitive dye imaging. Scientific Report – Nature 2020 .
- J. Kang, H. N. D. Le, S. Karakus, A. Burnett, J. U. Kang, E. M. Boctor, “Towards real-time intra-operative guidance using combined photoacoustic and pulsed fluorescence imaging for robotic-assisted surgery: preliminary in vivo experiment using murine prostate model,” SPIE Photonics West, 10484-8, San Francisco, USA, 29 Jan. 2018.
