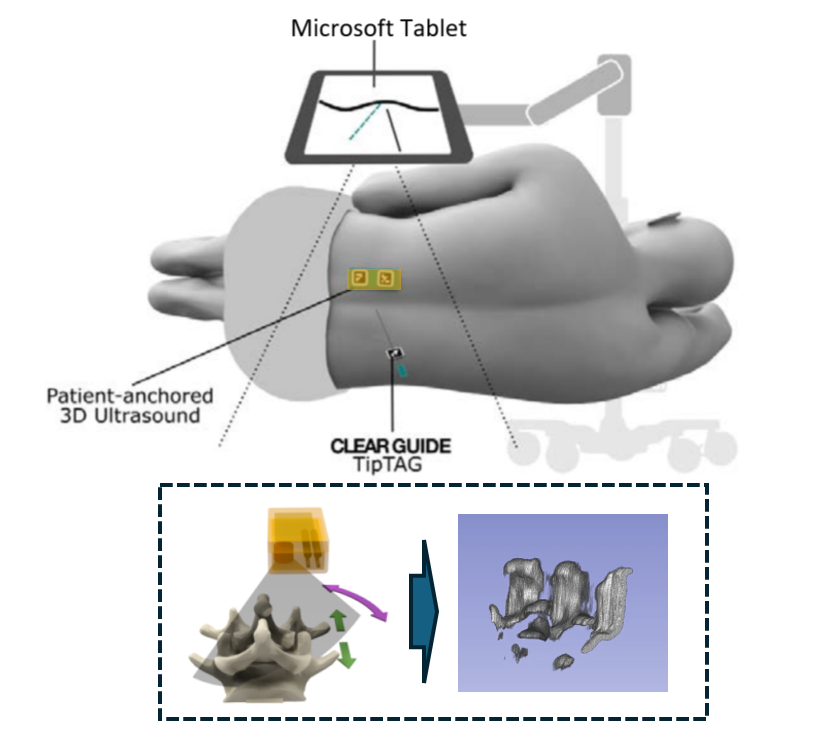
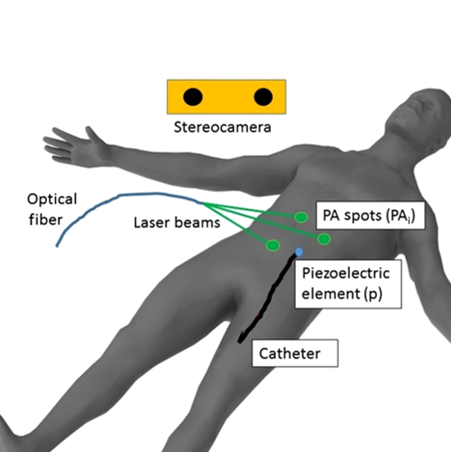
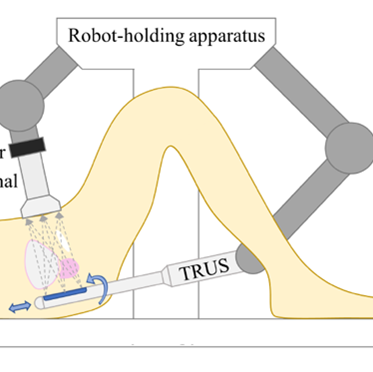
As one of the most commonly performed spinal interventions in routine clinical practice, lumbar punctures are usually done with only hand palpation and trial-and-error. Failures can prolong procedure time and introduce complications such as cerebrospinal fluid leaks and headaches. Therefore, in this work, we present a complete lumbar puncture guidance system with the integration of…
Category: Projects
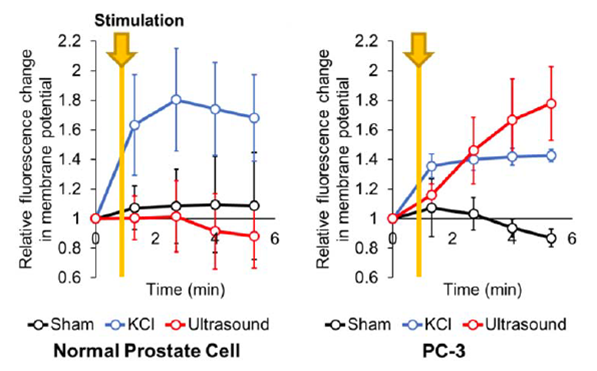
Although many studies suggested that cancerous prostate presents distinct membrane potential, there is currently no active translational research to turn this concept into cancer detection. One of the limitations is the fact that there is no established stimulation protocol and no non-invasive recording of the membrane potential. Ultrasound stimulation has the potential to be the…
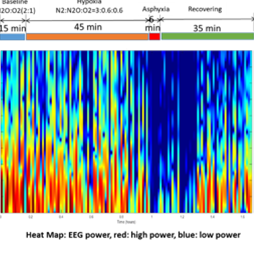
Our preliminary data suggest that neurons exposed to hypoxic injury respond differently to ultrasound-induced stimulation compared to sham treated neurons. Based on these findings we hypothesize that: non-invasive neuromodulation is a tool for functional evaluation of neural injury. The use of ultrasound neuromodulation as a functional interrogation tool to measure the severity of neural injury…
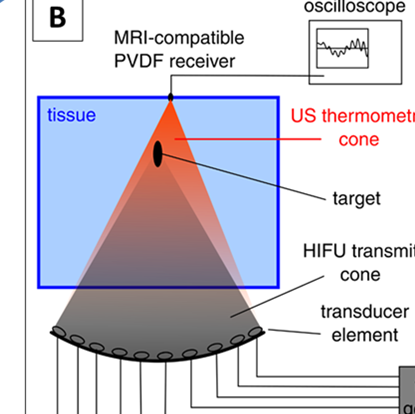
Our innovative research is focused on determining if US tomography-based thermometry in combination with thermal and acoustic modelling can be sufficient to replace MR thermometry and hence devising a system that can perform the same safe and effective uterine fibroid ablations without the need for costly MRI. Our developed system leverages existing HIFU systems by…
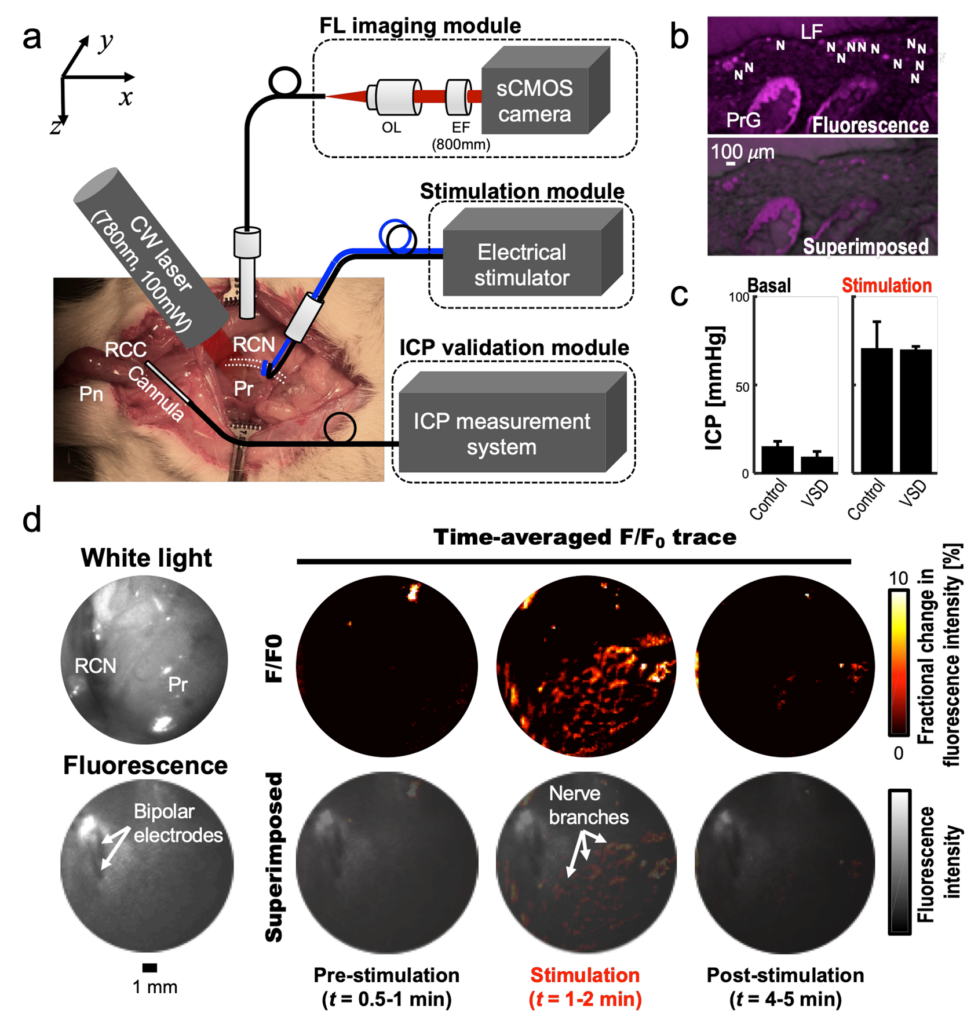
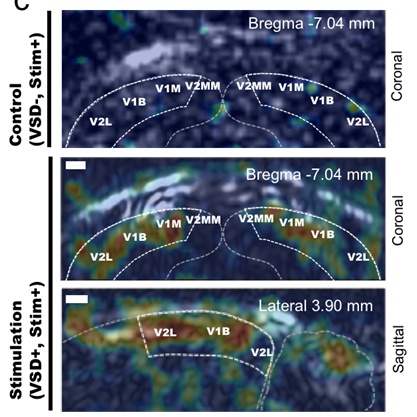
Sparing nerve during surgical procedure such as radical prostatectomy is crucial in minimizing post-operative complication. In this project, we aim to provide intra-operative functional nerve localization. Voltage-sensitive-dye imaging was developed by using fluorescence (FL) and photoacoustic (PA) imaging, where the optical contrast upon membrane potential variation was identified. In particular, PA imaging showed depth-profiling of…
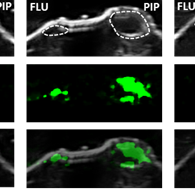
Needles, guidewires, and catheters represent some of the most used daily instruments by interventional radiologists. Catheters are commonly tracked with either an imaging modality such as X-ray fluoroscopy or a tracking system such as electromagnetic (EM) trackers. X-ray delivers a radiation dosage to the patient for a non-therapeutic purpose; and an EM tracker places certain…
We have developed a molecular PA imaging system capable of visualizing PSMA molecular contrast in vivo. We have designed a series of PA imaging contrast agents composed of three functional parts (Figure 1). The middle component is a linker that tethers the PSMA ligand to bulky optical dyes such as IRDye800CW, ICG, and Alexafluor750, which…
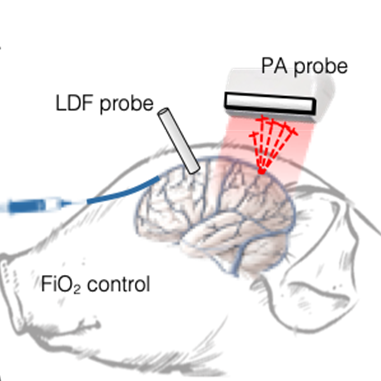
The feasibility of transcranial functional PA imaging of cerebral oxygenation in the piglet brain (5-day old, 2kg) was demonstrated (Figure 1a). Multi-spectral PA data were collected (700-900 nm in 10-nm intervals) while applying various fractional inspired oxygen (FiO2) levels to induce graded hypoxia. The ground-truth sO2 was also measured by direct sampling of venous blood…
PA imaging has a potential to sense the electrophysiological state of biological tissue. Voltage sensitive dyes are designed to monitor membrane potential by detecting fluorescence changes in response to neuronal or muscle electrical activity. Through our collaboration with Prof. Les Loew (University of Connecticut) who pioneered VSD synthesis, we have reported the first PA VSD…
Ultrasound computed tomography (USCT) offers quantitative anatomical tissue characterization for cancer detection. While most research and commercial development has focused on submerging target anatomy in a transducer-lined cylindrical water tank, this is not practical for imaging deep anatomy, so an alternative approach using aligned abdominal and endoluminal ultrasound probes is required. We propose a new…